Immun-Checkpoints
Immune checkpoint
T lymphocytes (T cells for short) are a central component of our immune system. They belong to the group of leukocytes (white blood cells). Along with B lymphocytes, they are the most important part of the acquired (adaptive) immune response.
The immune system is activated when a T-cell receptor (TCR) receives an appropriate signal.
This signal is a matching antigen, as in the lock-and-key principle. This antigen is presented by a special cell (APCs).
The reason for this is that T lymphocytes cannot simply recognize antigens. These antigens must be prepared beforehand. Subsequently, they are then presented on the MHC-encoded class I and class II receptors on the cell surface.
Thereby, the antigens are presented on the MHC-encoded class I and class II receptors on the cell surface.
To ensure that the reaction caused by this does not proceed in an uncontrolled manner, there are signals that can have an inhibitory or stimulatory effect:
On the cell surface (membrane) of T lymphocytes are receptors called immune checkpoints. Based on their influence on the immune response, they can be subdivided into anti-inflammatory (inhibitory) and proinflammatory (stimulatory) immune checkpoints.
Anti-inflammatory (inhibitory) immune checkpoints
| CTLA-4 | PD-1 | LAG3 | TIM-3 | NOX2 |
| KIT | VISTA | SIGLEC7 | B7-H3 | B7-H4 |
| BTLA | A2AR |
Proinflammatory (stimulatory) immune checkpoints
| CD27 | CD28 | CD40 | CD70 | CD86 |
| CD122 | CD134 (OX40) | CD137 | GITR | ICOS |
Table 1: Overview of some known immune checkpoint receptor-ligand pairings, their action and location.
| Effect | Function | T Cell | Antigen presenting cell (APC) | Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| anti-inflammatory | Receptor | BTLA | HVEM | Ligand |
| anti-inflammatory | Receptor | CTLA-4 | CD80(B7-H1) / CD86(B7-H2) | Ligand |
| anti-inflammatory | Receptor | TIGIT | CD155 | Ligand |
| anti-inflammatory | Receptor | PD-1 | PD-L1 | Ligand |
| anti-inflammatory | Receptor | PD-1 | PD-L2 | Ligand |
| anti-inflammatory | Receptor | TIM-3 | Galectin-9 | Ligand |
| anti-inflammatory | Receptor | LAG3 | MHC class II | Ligand |
| anti-inflammatory | Receptor | A2AR | - | Ligand |
| anti-inflammatory | Ligand/Receptor | VISTA | - | Ligand |
| anti-inflammatory | Ligand/Receptor | SIGLEC7 (CD328) | Sialylated glycans | Ligand |
| anti-inflammatory | Receptor | - | B7-H3 (CD276) | Ligand |
| anti-inflammatory | Receptor | - | B7-H4 | Ligand |
| proinflammatorisch | Receptor | GITR | GITRL | Ligand |
| proinflammatorisch | Receptor | OX40 | OX40L | Ligand |
| proinflammatorisch | Receptor | 4-1BB (CD137) | 4-1BBL | Ligand |
| proinflammatorisch | Receptor | CD27 | CD70 | Ligand |
| proinflammatorisch | Receptor | ICOS | ICOSL | Ligand |
| proinflammatorisch | Ligand | CD28 | CD80(B7-H1) / CD86(B7-H2) | Receptor |
| proinflammatorisch | Ligand | CD40L | CD40 | Receptor |
The corresponding counterparts to the receptors, the ligands, are found on the surface of other cells.
The interaction of the two helps the immune system avoid an immune response to the body's own cells.
If this interaction is disturbed, autoimmune diseases can occur, for example.
Tumor cells show significant overexpression of these receptor counterparts, allowing them to escape recognition by T cells. This phenomenon is also known as immune evasion.
Thus, the tumor cells camouflage themselves as "harmless", endogenous cells and are thus not recognized by the immune system.
Cancer immunotherapy (immune checkpoint therapy)
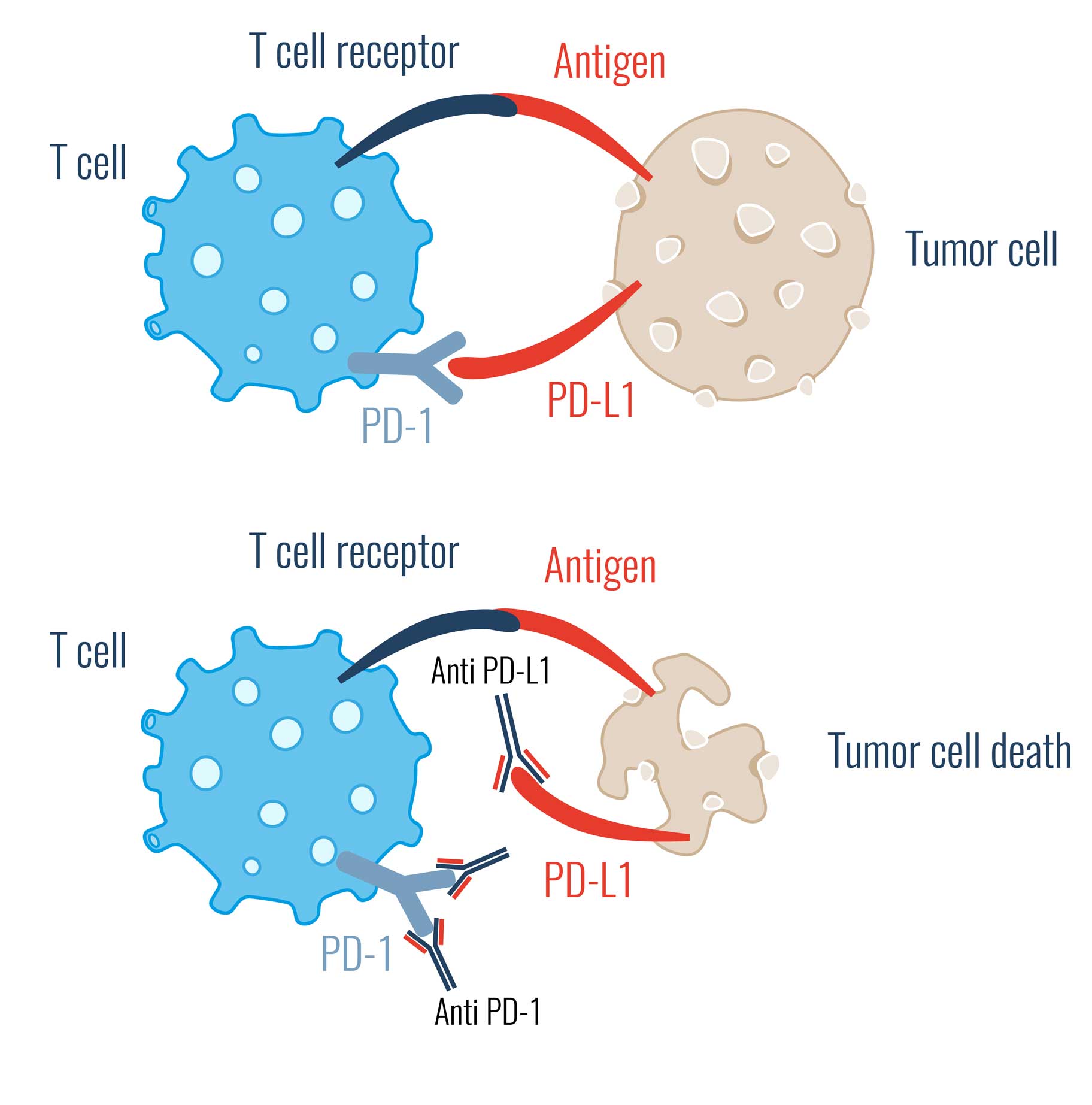
In medicine, the field of cancer immunotherapy (immune checkpoint therapy) deals with immune checkpoint inhibitors. These are substances e.g. in vivo antibodies, that bind to immune checkpoints, for example. In this way, they prevent the tumor cell from escaping recognition by T cells.
This prevents the interaction between the receptor and its ligand, and thus the cancer cell's "all-clear" signal is no longer passed on to the controlling immune cells.
The immune system now no longer falls for the cancer cells' camouflage.
Consequently, the body's immune response is aided in the fight against the tumor cell by immune checkpoint inhibitors.
Certainly, three immune checkpoints are particularly well known.
CTLA-4 inhibitors
CTLA-4 is a ligand found on the surface of T cells.
When CTLA-4 binds to CD80 or CD86, regulatory T cells are "turned off" and thus become inactive.
Inhibition of CTLA-4 therefore causes immune cells not to become inactive and continue to target cancer cells.
PD-1 inhibitors
PD-1 is a surface receptor on T cells.
In the healthy environment, PD-1 serves as a protective mechanism against immune system overreaction. Again, PD-1 can be seen as a kind of "off" switch.
A cancer cell can use this switch to prevent an immune reaction against itself. But if you block this switch with a PD-1 inhibitor, you effectively take the fuse out: no matter how many times you use the switch, nothing happens.
PD-L1 Inhibitors
PD-L1 is the trigger of PD-1 signaling. If PD-L1 is now blocked, no "off" signal can be triggered.
The best-known immune checkpoints include PD-1 and CTLA-4. James P. Allison and Tasuku Honjo received the Nobel Prize in Medicine in 2018 for their research in the field of immune checkpoints. The two inhibitors nivolumab and ipilimumab were developed against these immune checkpoints and have already been approved for clinical use.
VISTA
The monoclonal antibody (13F3) binds to the murine immune checkpoint "V-domain Immunoglobulin Suppressor of T cell Activation" (VISTA), also known as PD-1H and B7-H5. VISTA is a negative immune checkpoint that inhibits cytokine production by T cells and their proliferation. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (myeloid cells and regulatory T cells) exhibit marked overexpression of VISTA on their cell surface, inhibiting cytokine production and proliferation of T cells more than under normal physiological conditions. In several preclinical studies, specific blocking of VISTA, using the 13F3 monoclonal antibody, has resulted in delayed tumor growth. Furthermore, inhibition of the immune checkpoint VISTA is being investigated for the treatment of solid tumors and lymphomas in humans in clinical trials. This therapeutic approach represents a promising approach for future cancer immunotherapy.
References regarding clone 13F3:



