Array Assays
Overview
- Microarrays
- DNA Microarrays
- Protein Microarrays
- Antibody Microarrays
- Cytokine Microarrays
- Importance of cytokines in biomedical research
- How a cytokine array assay works
- Advantages of cytokine array assays
- Use of cytokine array assays
- Cytokine Array Assays from Raybiotech
- Multiplex Bead Array Assays
- Frequently Asked Questions
Microarrays
Microarrays are assays that allow the parallel analysis of more than a thousand individual detections.
Particularly useful is the fact that very small amounts of biological samples are sufficient to perform this analysis.
DNA Microarrays
DNA microarrays allow the detection of DNA.
This allows the analysis of gene expression levels within biological samples.
The transcription of genes first occurs in mRNA. In a DNA microarray, reverse transcriptase is used to transcribe the cellular RNA into cDNA. Subsequently, this cDNA can form a DNA-DNA hybrid bond with DNA probes immobilized on the carrier surface.
With regard to these probes, a DNA microarray can be classified even more precisely: While "spotted microarrays" use full-length cDNA, or PCR product fragments, "oligonucleotide microarrays" use short oligonucleotide sequences.
Protein Microarrays
In contrast to DNA microarrays, small amounts of a protein are immobilized on the carrier material in a protein microarray.
Antibody Microarrays
Antibody microarrays are a special form of protein microarrays.
Similar to an ELISA, a detection antibody is fixed on the carrier material.
After successful incubation with the biological sample, the interaction between the fixed antibody and the target antigen within the sample can be detected.
While a DNA microarray examines gene expression, an antibody microarray can be used to analyze protein expression.
A cytokine array is a special form of antibody microarray in which the analytes to be detected are all from the cytokine group.
Cytokine microarrays
Using a cytokine array assay, the expression level of up to 200 different cytokines can be determined in a small sample size with only one experiment.
Cytokines are a group of proteins with an important function in immunological reactions. Among other things, they have a regulatory effect on the growth and differentiation of cells. Cytokines are divided into five main groups: Chemokines, tumor necrosis factors, interleukins, interferons and colony stimulating factors.
Importance of cytokines in biomedical research
Many biological processes such as apoptosis, inflammation, new blood vessel formation (angiogenesis), and immune responses can influence the expression level of cytokines. Furthermore, various diseases such as cancer, arthritis, atherosclerosis, obesity, diabetes and infections show altered cytokine profiles. Therefore, the quantitative determination of cytokines and thus cytokine array assays are given an important role in biomedical, drug and biomarker research.
While the global expression level of genes is comparatively easy to measure using cDNA microarrays, this has been very complicated, costly and time-consuming for proteins. The cytokine array assay system now enables simultaneous measurement of protein expression levels within a few hours and at low cost.
How a cytokine array assay works
The technology of cytokine array assays is based on the principle of a „Sandwich-ELISA“ (see figure).
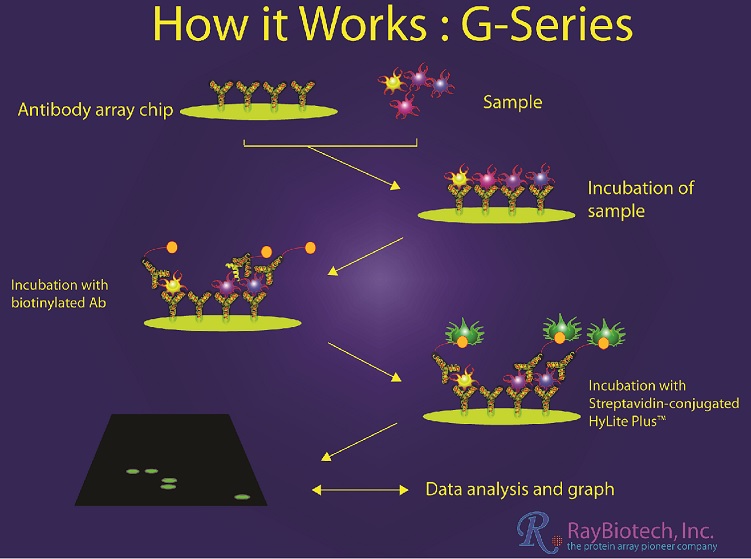
Specific antibodies used for the detection of cytokines are attached to a membrane in different circular fields (spots). These immobilized antibodies form the solid phase of the assay.
By incubating the membrane with the sample to be tested, the cytokines contained therein are bound by the corresponding antibodies and thus fixed on the membrane.
In the next step, a biotin-coupled second antibody is used to label the antibody-cytokine complex on the membrane, creating the so-called "sandwich complex" of first antibody-cytokine-second antibody.
Various marker molecules can be bound to the complex via biotin, which can then be visualized by chemiluminescence, colorimetry or infrared fluorescence, allowing the data to be analyzed and interpreted.
Advantages of cytokine array assays
- Simultaneous detection of different cytokines in a single experiment.
- No additional equipment required.
- High sensitivity allows detection of most proteins in the pg range.
- Less than 100 µl of sample is required to measure over 174 cytokines.
- Inexpensive for routine use.
- Easy to perform even without experience.
- Product diversity: human, mouse, rat.
- Different biological samples can be measured.
- High variability: cytokine array assays can be custom made.
Use of cytokine array assays
- Expression profiling of cytokines
- Monitoring cytokine levels in clinical trials
- Identification of potential molecules for drug development
- Identification of potential mechanisms for drug action
- Detection of biomarkers for disease treatment
- Identification of expression patterns for molecular classification of diseases
Cytokine Array Assays from Raybiotech
| Name | Product No. | Quantity | Series |
| RayBio® Human Cytokine Antibody Array 1 | AAH-CYT-1 | 2 Sample Kit | C-Series |
| RayBio® Human Cytokine Antibody Array 4 | AAH-CYT-4 | 2 Sample Kit | C-Series |
| RayBio® Human Cytokine Antibody Array 5 | AAH-CYT-5 | 2 Sample Kit | C-Series | RayBio® Human Cytokine Antibody Array 6 | AAH-CYT-6 | 2 Sample Kit | C-Series | RayBio® Human Cytokine Antibody Array 7 | AAH-CYT-7 | 2 Sample Kit | C-Series | RayBio® Human Cytokine Antibody Array 8 | AAH-CYT-8 | 2 Sample Kit | C-Series | RayBio® Human Cytokine Antibody Array 9 | AAH-CYT-9 | 2 Sample Kit | C-Series | RayBio® Human Cytokine Antibody Array 10 | AAH-CYT-10 | 2 Sample Kit | C-Series | RayBio® Human Inflammation Antibody Array 3 | AAH-INF-3 | 2 Sample Kit | C-Series | RayBio® Human Angiogenesis Antibody Array 1 | AAH-ANG-1 | 2 Sample Kit | C-Series | RayBio® Human Atherosclerosis Antibody Array 1 | AAH-ATH-1 | 2 Sample Kit | C-Series | RayBio® Human Matrix Metalloproteinase Antibody Array 1 | AAH-MMP-1 | 2 Sample Kit | C-Series | RayBio® Human Chemokine Antibody Array 1 | AAH-CHE-1 | 2 Sample Kit | C-Series | RayBio® Human Growth Factor Antibody Array 1 | AAH-GF-1 | 2 Sample Kit | C-Series |
To learn more about the correct use of each array assay, please refer to the attached working instructions of the respective product.
![]() In this Video of Raybiotech you will learn more about the function of Array Assays.
In this Video of Raybiotech you will learn more about the function of Array Assays.
Multiplex Bead Array Assays
Multiplex bead array assays are very similar to a microarray.
However, a multiplex assay uses magnetic beads for parallel detection of analytes. Unlike a microarray, these are not immobilized on the support material. The detection antibodies are located on these beads.
For example, beads with different diameters can be used and coupled with different detection antibodies.
This has the useful advantage that the proteins bound by the antibody-coupled bead can be analyzed within a flow cytometer.
Frequently asked questions
What is array-based sequencing?
Array-based sequencing combines array-based sequence capture with next-generation sequencing. Using a DNA microarray, the results of specific gene expressions can thus be separated and subsequently sequenced.
How do microarrays work?
A microarray is based on binding between a fixed DNA probe and a DNA fragment within the sample. In this process, DNA-DNA hybridization takes place. In this way, specific DNA fragments are captured and can be visualized by fluorescence.
Is ELISA a microarray?
An ELISA is not a microarray, however antibody microarrays are based on the same principle. Both use a detection antibody with which specific analytes can be bound.
What is a gene array?
A gene array helps in the detection of specific genes. For this purpose, nucleic acids are fixed on the carrier material, which hybridize with a sample containing nucleic acids, thus allowing their detection.



